Chances are you have a Wi-Fi network at home, or live close to one (or more) that tantalizingly pops up in a list whenever you boot up the laptop.
The problem is, if there's a lock next to the network name (AKA the SSID, or service set identifier), that indicates security is activated. Without the password or passphrase, you're not going to get access to that network, or the sweet, sweet internet that goes with it.
Perhaps you forgot the password on your own network, or don't have neighbors willing to share the Wi-Fi goodness. You could just go to a café, buy a latte, and use the "free" Wi-Fi there. Download an app for your phone like WiFi-Map (available for iOS and Android), and you'll have a list of over 2 million hotspots with free Wi-Fi for the taking (including some passwords for locked Wi-Fi connections, if they're shared by any of the app's 7 million users).
However, there are other ways to get back on the wireless. Some require such extreme patience and waiting that the café idea is going to look pretty good. Read on if you can't wait.
Windows Commands to Get the Key
This trick works to recover a Wi-Fi network password (aka network security key) only if you've previously attached to the Wi-Fi in question using that very password. In other words, it only works if you've forgotten a previously used password.
It works because Windows 8 and 10 create a profile of every Wi-Fi network to which you attach. If you tell Windows to forget the network, then it also forgets the password, so this won't work. But most people never explicitly do that.
It requires that you go into a Windows Command Prompt with administrative privileges. To do so, use Cortana to search for "cmd" and the menu will show Command Prompt; right-click that entry and select "Run as administrator." That'll open the black box full of white text with the prompt inside—it's the line with a > at the end, probably something like C:\WINDOWS\system32\>. A blinking cursor will indicate where you type. Start with this:
netsh wlan show profile
The results will bring up a section called User Profiles—those are all the Wi-Fi networks (aka WLANs, or wireless local area networks) you've accessed and saved. Pick the one you want to get the password for, highlight it, and copy it. At the prompt below, type the following, but replace the Xs with the network name you copied; you only need the quotation marks if the network name has spaces in it.
netsh wlan show profile name="XXXXXXXX" key=clear
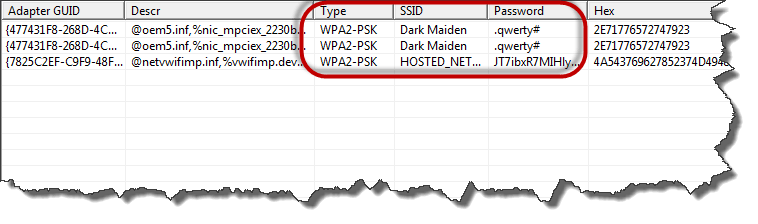
In the new data that comes up, look under Security Settings for the line "Key Content." The word displayed is the Wi-Fi password/key you are missing.
On macOS, open up the Spotlight search (Cmd+Space) and type terminal to get the Mac equivalent of a command prompt. Type the following, replacing the Xs with the network name.
security find-generic-password -wa XXXXX
Reset the Router
Before you do a full router reset just to get on the wireless, try to log into the router first. From there, you can easily reset your Wi-Fi password/key if you've forgotten it.
That's not possible if you don't know the password for the router, either. (They're not the same thing unless you set it up that way). Resetting the router only works if you have access. That access could be over Wi-Fi (which we've just established you don't have) or physically utilizing an Ethernet cable.
Or that access can simply be that you are in the same room as the router. Almost every router in existence has a recessed reset button. Push it with a pen or unfolded paperclip, hold it for about 10 seconds, and the router will reset to the factory settings.
If you've got a router that came from your internet service provider (ISP), check the stickers on the unit before a reset—the ISP might have printed the router and Wi-Fi key right on the hardware.
Once a router is reset, you need another password (plus a username) to access the router itself. Again, you can do this via a PC attached to the router via Ethernet—you'll need that since the reset probably killed any potential Wi-Fi connection you had going in. The actual access is typically done with a web browser.
The URL to type is either 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, or some variation. Try them randomly; that generally works. To figure out which one, on the PC connected to the router, open a command prompt and type "ipconfig" without the quotes. Look among the gobbledygook for an "IPv4 Address," which will start with 192.168. The other two spaces, called octets, are going to be different numbers between 0 and 255. Note the third octet (probably a 1 or 0). The fourth is specific to the PC you're using to log into the router.
In the browser, type 192.168.x.1, replacing the X with the number you found in the ipconfig search. The 1 in the last octet should point at the router—it's the number one device on the network.
At this point, the router should then ask for a username and password. You can check your manual, but you probably lost it or threw it away. So instead, go to RouterPasswords.com, which exists for one reason: to tell people the default username/password on every router ever created.
You'll need the router's model number, but that's easy enough to find on the back or bottom. You'll quickly see a pattern among router makers of having the username of admin and a password of password. Since most people are lazy and don't change an assigned password, you could try those options before hitting the reset button. (But c'mon, you're better than that—change the password when you access the router's settings via your web browser.)
Once you've accessed the router interface, go to the Wi-Fi settings, turn on the wireless networks, and assign strong but easy-to-recall passwords. After all, you don't want to share with neighbors without your permission.
Make that Wi-Fi password easy to type on a mobile device, too. Nothing is more frustrating than trying to get a smartphone on Wi-Fi with some cryptic, impossible to key-in-via-thumbs nonsense, even if it is the most secure.
Crack the Code
You didn't come here because the headline said "reset the router," though. You want to know how to crack the password on a Wi-Fi network.
Searching on "wi-fi password hack," or other variations, nets you a lot of links—mostly for software on sites where the adware and bots and scams are pouring like snake oil. Download them at your own risk, for Windows PCs especially. It's best to have a PC that you can afford to get effed up a bit if you go that route. I had multiple attempts with tools I found just get outright deleted by my antivirus before I could even try to run the EXE installation file.
You could create a system just for this kind of thing, maybe dual-boot into a separate operating system that can do what's called "penetration testing"—a form of offensive approach security, where you examine a network for any and all possible paths of a breach. Kali Linux is a Linux distribution built for just that purpose. You can run Kali Linux off a CD or USB key without even installing it to your PC's hard drive. It's free and comes with all the tools you'd need to crack a network. It even now comes as an app for Windows 10 in the Windows App Store! If you're only after a Wi-Fi network, the Wifislax distro is a Live CD targets them directly.
If you don't want to install a whole OS, then try the tried-and-true tools of Wi-Fi hackers.
Aircrack has been around for years, going back to when Wi-Fi security was only based on WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). WEP was weak even back in the day and was supplanted in 2004 by WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access).
Aircrack-ng—labeled as a "set of tools for auditing wireless networks," so it should be part of any network admin's toolkit—will take on cracking WEP and WPA-PSK keys. It comes with full documentation, but it's not simple. To crack a network you need to have the right kind of Wi-Fi adapter in your computer, one that supports packet injection. You need to be comfortable with the command line and have a lot of patience. Your Wi-Fi adapter and Aircrack have to gather a lot of data to get anywhere close to decrypting the passkey on the network you're targeting. It could take a while. Here's a how-to on doing it using Aircrack installed on Kali Linux. Another option on the PC using the command line is Airgeddon.
If you prefer a graphical user interface (GUI), there is KisMAC for macOS. It's mainly known as a "sniffer" for seeking out Wi-Fi networks. It's the kind of thing we don't need much of these days since our phones and tablets do a pretty good job of showing us every Wi-Fi signal in the air around us. But, it can crack some keys with the right adapter installed. Also on the Mac: Wi-Fi Crack. To use those, or Aircrack-ng on the Mac, you need to install them using MacPorts, a tool for installing command-line products on the Mac.
Cracking the much stronger WPA/WPA2 passwords and passphrases is the real trick.
Reaver-wps is the one tool that appears to be up to the task. You'll need that command-line comfort again to work with it. After two to 10 hours of brute force attacks, Reaver should be able to reveal a password... but it's only going to work if the router you're going after has both a strong signal and WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) turned on. WPS is the feature where you can push a button on the router, another button on a Wi-Fi device, and they find each other and link auto-magically, with a fully encrypted connection. It's also the "hole" through which Reaver crawls.