Intel HD Graphics Driver 26.20.100.7158 for Windows 10 64-bit
Installs the HD Graphics Driver for Windows 10 version, also works for Windows 8/7 64-bit.
This is the recommended driver for the early access release of the brand-new Intel® Graphics Command Center. If not already installed, this driver will add the Intel® Graphics Command Center to the system.
The Intel Graphics Command Center (IGCC) is a software interface that provides consumers a modern design to optimize their visual experience – built on community feedback, and designed for simplicity and ease of use:
IGCC scans for installed games to provide 1-click optimization of in-game settings based on the user’s hardware, and the ability to create custom game profiles to directly tune individual game settings.
Additionally, IGCC helps consumers understand graphics settings with simple explanations and before-and-after images to recognize how each setting will tax their hardware.
What's New:
Launch driver for:
- eFootball Pro Evolution Soccer 2020*
- Greedfall*
- 10th Gen Intel Core processors with UHD Graphics (“Comet Lake”)
Improvements:
- Enabling driver for Pro Evolution Soccer 2020*, Greedfall*, Children of Morta*, Spyro Reignited Trilogy*, and Pagan Online*.
- Performance optimizations for Age of Wonders: Planetfall*.
- OpenCL optimizations.
- More efficient content protection.
Developer highlights:
- Enabled reporting support for the following OpenGL 4.6 SPIR-V extensions:
- SPV_KHR_shader_ballot
- SPV_KHR_shader_draw_parameters
- SPV_KHR_storage_buffer_storage_class
- SPV_KHR_subgroup_vote
- Enabled the following Vulkan extensions:
- VK_EXT_fragment_shader_interlock
- VK_EXT_buffer_device address
- VK_EXT_separate_stencil_usage
- VK_KHR_uniform_buffer_standard_layout
Important Note:
These new drivers labeled as Windows DCH graphics drivers are not backward compatible with our previous graphics drivers that we're now labeling Legacy. This means if later you want to revert to a Legacy driver you will need to uninstall the driver via Windows Apps and Features and reboot the system before installing a Legacy driver. Failure to do so may result in minor to catastrophic issues on your system as well as system instability.
DO NOT use the INF / Have-Disk method to install or uninstall this driver as it bypasses the Intel installer designed to install these new drivers, thereby possibly resulting in minor to major system instability. For this reason, we're not providing the ZIP file for the next several driver releases while users transition to this new Microsoft driver platform.
Supported Products:
Hardware
All platforms with the following configurations are supported:
- 10th Gen Intel Core processors with UHD Graphics (“Comet Lake”)
- 7th Generation Intel Core processors with Intel Iris Plus Graphics 640/650
- 7th Generation Intel Core processors with Intel HD Graphics 610/615/620/630
- Intel Xeon processor E3-1500M v5 family with Intel HD Graphics P630
- Pentium Processors with Intel HD Graphics 610
- 6th Generation Intel Core processors with Intel Iris Pro Graphics 580
- 6th Generation Intel Core processors with Intel Iris Graphics 540/550
- 6th Generation Intel Core processors with Intel HD Graphics 520/530
- Intel Xeon processor E3-1500M v5 family with Intel HD Graphics P530
- Intel Xeon processor E3-1500M v5 family with Intel Iris Pro Graphics P580
- Intel Core M processors with Intel HD Graphics 515
- Pentium and Celeron Processors with Intel HD Graphics 500/505
- Pentium Processors with Intel HD Graphics 510
On 7th Generation Intel Core processors and related Pentium/Celeron:
- Microsoft Windows 10 64-bit
On 6th Generation Intel Core and Intel Mobile Xeon processors and related Pentium/Celeron:
- Microsoft Windows 10 64-bit
- Microsoft Windows 8.1* 64-bit
- Microsoft Windows 7* 64-bit
Support included but limited to the following chips:
- Intel Core i3-10110U Processor (4M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6006U Processor (3M Cache, 2.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6098P Processor (3M Cache, 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6100 Processor (3M Cache, 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6100E Processor (3M Cache, 2.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6100H Processor (3M Cache, 2.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6100T Processor (3M Cache, 3.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6100TE Processor (4M Cache, 2.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6100U Processor (3M Cache, 2.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6102E Processor (3M Cache, 1.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6157U Processor (3M Cache, 2.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6167U Processor (3M Cache, 2.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6300 Processor (4M Cache, 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6300T Processor (4M Cache, 3.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-6320 Processor (4M Cache, 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7020U Processor (3M Cache, 2.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7100 Processor (3M Cache, 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7100E Processor (3M Cache, 2.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7100H Processor (3M Cache, 3.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7100T Processor (3M Cache, 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7100U Processor (3M Cache, 2.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7101E Processor (3M Cache, 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7101TE Processor (3M Cache, 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7102E Processor (3M Cache, 2.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7130U Processor (3M Cache, 2.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7167U Processor (3M Cache, 2.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7300 Processor (4M Cache, 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7300T Processor (4M Cache, 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7320 Processor (4M Cache, 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7350K Processor (4M Cache, 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8100 Processor (6M Cache, 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8100B Processor (4M Cache, 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8100H Processor (6M Cache, 3.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8100T Processor (6M Cache, 3.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8109U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8121U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8130U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8145U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8300 Processor (8M Cache, 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8300T Processor (8M Cache, 3.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-8350K Processor (8M Cache, 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-9100 Processor (6M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-9100E Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-9100HL Processor (6M Cache, up to 2.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-9100T Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-9100TE Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-9300 Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-9300T Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-9320 Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i3-9350K Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5+8400 Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.00 GHz) includes Intel Optane Memory (16GB)
- Intel Core i5+8500 Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz) includes Intel Optane Memory (16GB)
- Intel Core i5-10210U Processor (6M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6198DU Processor (3M Cache, up to 2.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6200U Processor (3M Cache, up to 2.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6260U Processor (4M Cache, up to 2.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6267U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6287U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6300HQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6300U Processor (3M Cache, up to 3.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6350HQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6360U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6400 Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6400T Processor (6M Cache, up to 2.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6402P Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6440EQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6440HQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6442EQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 2.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6500 Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6500T Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6500TE Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6585R Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6600 Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6600K Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6600T Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-6685R Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7200U Processor (3M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7260U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7267U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7287U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7300HQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7300U Processor (3M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7360U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7400 Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7400T Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7440EQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7440HQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7442EQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 2.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7500 Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7500T Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7600 Processor (6M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7600K Processor (6M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7600T Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7Y54 Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-7Y57 Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8200Y Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8210Y Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8250U Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8259U Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8265U Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8269U Processor (6M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8300H Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8305G Processor with Radeon Pro WX Vega M GL graphics (6M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8305G Processor with Radeon RX Vega M GL graphics (6M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8350U Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8400 Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8400B Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8400H Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8400T Processor (9M Cache, up to 3.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8500 Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8500B Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8500T Processor (9M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8600 Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8600K Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-8600T Processor (9M Cache, up to 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9300H Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9400 Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9400H Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9400T Processor (9M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9500 Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9500E Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9500T Processor (9M Cache, up to 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9500TE Processor (9M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9600 Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9600K Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i5-9600T Processor (9M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i7+8700 Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.60 GHz) includes Intel Optane Memory (16GB)
- Intel Core i7-10510U Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-10710U Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.7 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6498DU Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6500U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6560U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6567U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6600U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6650U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6660U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6700 Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6700HQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6700K Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6700T Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6700TE Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6770HQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6785R Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6820EQ Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6820HK Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6820HQ Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6822EQ Processor (8M Cache, up to 2.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6870HQ Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6920HQ Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6970HQ Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7500U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.50 GHz )
- Intel Core i7-7560U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7567U Processor (4M Cache, up to 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7600U Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7660U Processor (4M Cache, up to 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7700 Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7700HQ Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7700K Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7700T Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7820EQ Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7820HK Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7820HQ Processor (8M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7920HQ Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7Y75 Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8086K Processor (12M Cache, up to 5.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8500Y Processor (4M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8550U Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8559U Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8565U Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8650U Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8700 Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8700B Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8700K Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8700T Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.00 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8705G Processor with Radeon RX Vega M GL graphics (8M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8706G Processor with Radeon Pro WX Vega M GL graphics (8M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8706G Processor with Radeon RX Vega M GL graphics (8M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8709G Processor with Radeon RX Vega M GH graphics (8M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8750H Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8809G Processor with Radeon RX Vega M GH graphics (8M Cache, up to 4.20 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-8850H Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-9700 Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.70 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-9700E Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-9700K Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.90 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-9700T Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.30 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-9700TE Processor (12M Cache, up to 3.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-9750H Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.50 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-9850H Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.60 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-9850HE Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.40 GHz)
- Intel Core i7-9850HL Processor (9M Cache, up to 4.10 GHz)
- Intel Core i9-8950HK Processor (12M Cache, up to 4.80 GHz)
- Intel Core i9-9900K Processor (16M Cache, up to 5.00 GHz)
- Intel Core m3-6Y30 Processor (4M Cache, up to 2.20 GHz)
- Intel Core m3-7Y30 Processor (4M Cache, 2.60 GHz )
- Intel Core m3-7Y32 Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.00 GHz)
- Intel Core m3-8100Y Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.40 GHz)
- Intel Core m5-6Y54 Processor (4M Cache, up to 2.70 GHz)
- Intel Core m5-6Y57 Processor (4M Cache, up to 2.80 GHz)
- Intel Core m7-6Y75 Processor (4M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
- Intel HD Graphics 500
- Intel HD Graphics 505
- Intel HD Graphics 510
- Intel HD Graphics 515
- Intel HD Graphics 520
- Intel HD Graphics 530
- Intel HD Graphics 610
- Intel HD Graphics 615
- Intel HD Graphics 620
- Intel HD Graphics 630
- Intel HD Graphics for 6th Generation Intel Processors
- Intel HD Graphics P530
- Intel HD Graphics P630
- Intel Iris Graphics 540
- Intel Iris Graphics 550
- Intel Iris Plus Graphics 640
- Intel Iris Plus Graphics 645
- Intel Iris Plus Graphics 650
- Intel Iris Plus Graphics 655
- Intel Iris Pro Graphics 580
- Intel Iris Pro Graphics P580
- Intel UHD Graphics
- Intel UHD Graphics 600
- Intel UHD Graphics 605
- Intel UHD Graphics 610
- Intel UHD Graphics 615
- Intel UHD Graphics 617
- Intel UHD Graphics 620
- Intel UHD Graphics 630
- Intel UHD Graphics P630
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1505L v5 (8M Cache, 2.00 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1505M v5 (8M Cache, 2.80 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1515M v5 (8M Cache, 2.80 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1535M v5 (8M Cache, 2.90 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1545M v5 (8M Cache, 2.90 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1558L v5 (8M Cache, 1.90 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1565L v5 (8M Cache, 2.50 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1575M v5 (8M Cache, 3.00 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1578L v5 (8M Cache, 2.00 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1585 v5 (8M Cache, 3.50 GHz)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1585L v5 (8M Cache, 3.00 GHz)
- Radeon Pro WX Vega M GL Graphics
- Radeon RX Vega M GH Graphics
- Radeon RX Vega M GL Graphics
Supported OS versions
- Microsoft Windows 10-64 - Fall Creators Update (1709)
- Microsoft Windows 10-64 - April 2018 Update (1803)
- Microsoft Windows 10-64 - October 2018 Update (1809)
Intel HD Graphics Driver 26.20.100.7158 for Windows 10 64-bit
"Run as Administrator": What Does It Mean?
Why Do Some Programs Need to be Run as Administrator & What Happens When You Do?.
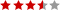
As a Pctoolsword reader you've surely opened software as an admin on Windows before -- maybe as recently as today -- so the function probably isn't foreign to you. However, we were curious to know more about what happens under the hood of Windows when you tell the operating system to run a program as an administrator, and why this process is necessary in the first place.
Those of you who made the transition from XP to Vista will probably remember the introduction of "User Access Control" (UAC) or "Mandatory Integrity Control" (MIC). The security feature, which remains part of Microsoft's OS, prompts you when software tries making changes to your system and rests at crux of why applications sometimes require "elevated" access.
When you log in to Windows, your account is assigned a token that contains identifying information including your user groups and privileges such as read, write, and execute permissions.
Among the information in that token is an integrity level which is used by the operating system determine the trustworthiness of objects like files, registry keys for the purpose of informing users when installations are being launched as well as isolating processes from having unnecessary access to system files.
Editor's Note: This feature was originally published on October 8, 2018. It's just as relevant and current today as it was then, so we've bumped it as part of our #ThrowbackThursday initiative.
The Windows Mandatory Integrity Control (MIC) mechanism has at least six different integrity levels: untrusted, low, medium, high, system and trusted installer.
By default, a standard user account has a medium integrity, which is the maximum level available for a process to be created when you open an executable file without providing elevated access via admin credentials.
When you right-click on a file or program and choose "Run as administrator," that process (and only that process) is started with an administrator token, thus providing high integrity clearance for features that may require the additional access to your Windows files etc.
The different Windows integrity levels:
- Untrusted Integrity: Given to anonymous processes.
- Low Integrity: Commonly used for Web-facing software such as browsers.
- Medium Integrity: Applied to standard users and used for most objects.
- High Integrity: Administrator-level access, generally requires elevation.
- System Integrity: Reserved for the Windows kernel and core services.
- Trusted Installer: Used for Windows Updates and system components.
Processes started by opening an exe from a Windows account with medium clearance will have that integrity level unless the executable file is set to low, and developers are encouraged to use the lowest access possible, ideally avoiding instances where software will require high integrity to thwart unauthorized code (malware) from taking root.
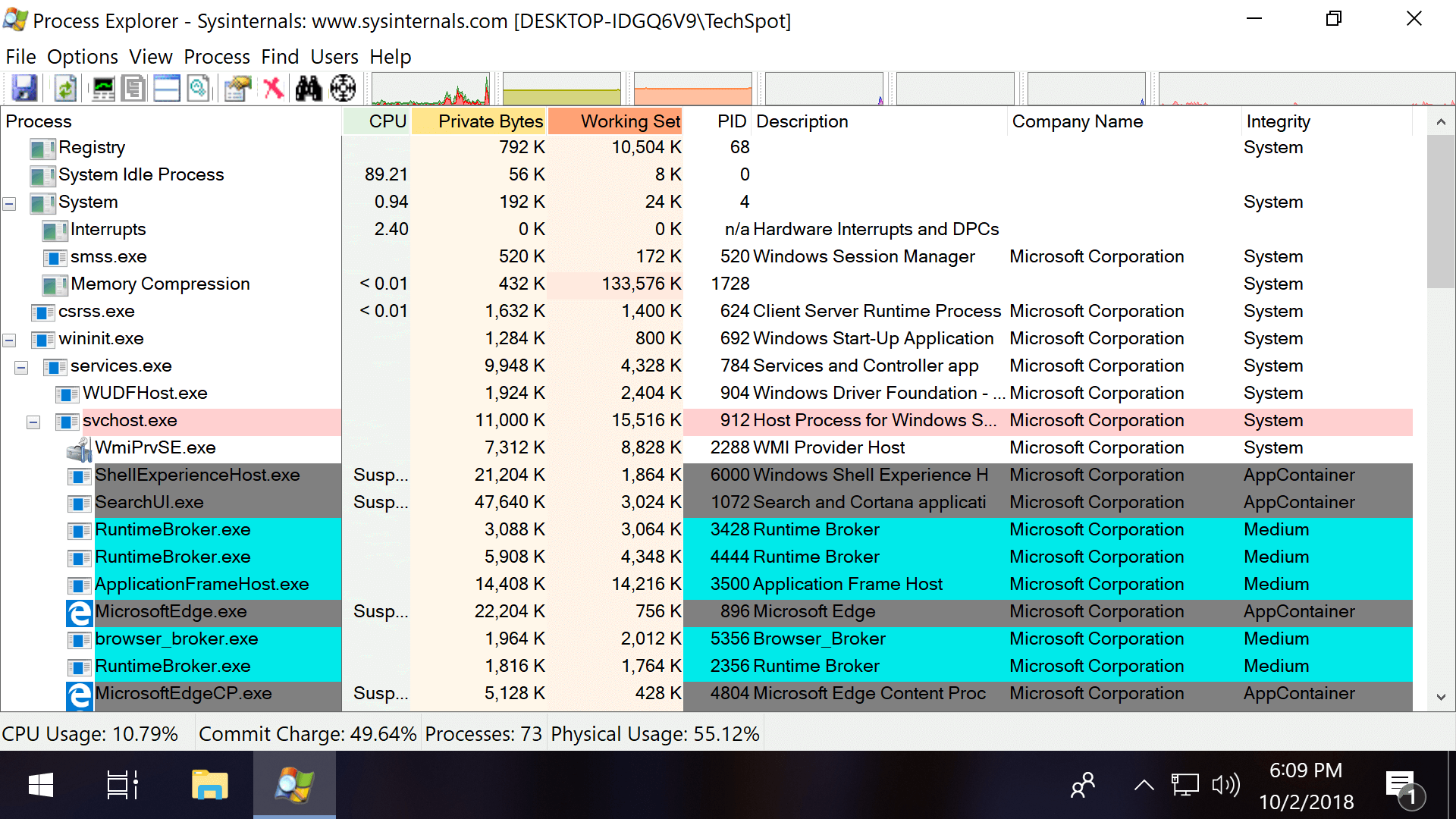
The practice of "least-privilege" design is applied to Windows' own administrator accounts, which receive both standard and admin-level tokens upon logging in, using standard/medium integrity access when possible instead of high.
Although Microsoft recommends against running programs as an administrator and giving them high integrity access without a good reason, new data must be written to Program Files for an application to be installed which will always require admin access with UAC enabled, while software such as AutoHotkey scripts will often need elevated status to function properly.
Here are all the ways we could find to open executable files with administrator access (high integrity) on Windows 10, including some methods that will configure software to always open with elevated access:
Ways to run a program as an administrator on Windows
Starting with the most obvious: you can launch a program as an administrator by right-clicking on the executable file and choosing "Run as administrator."
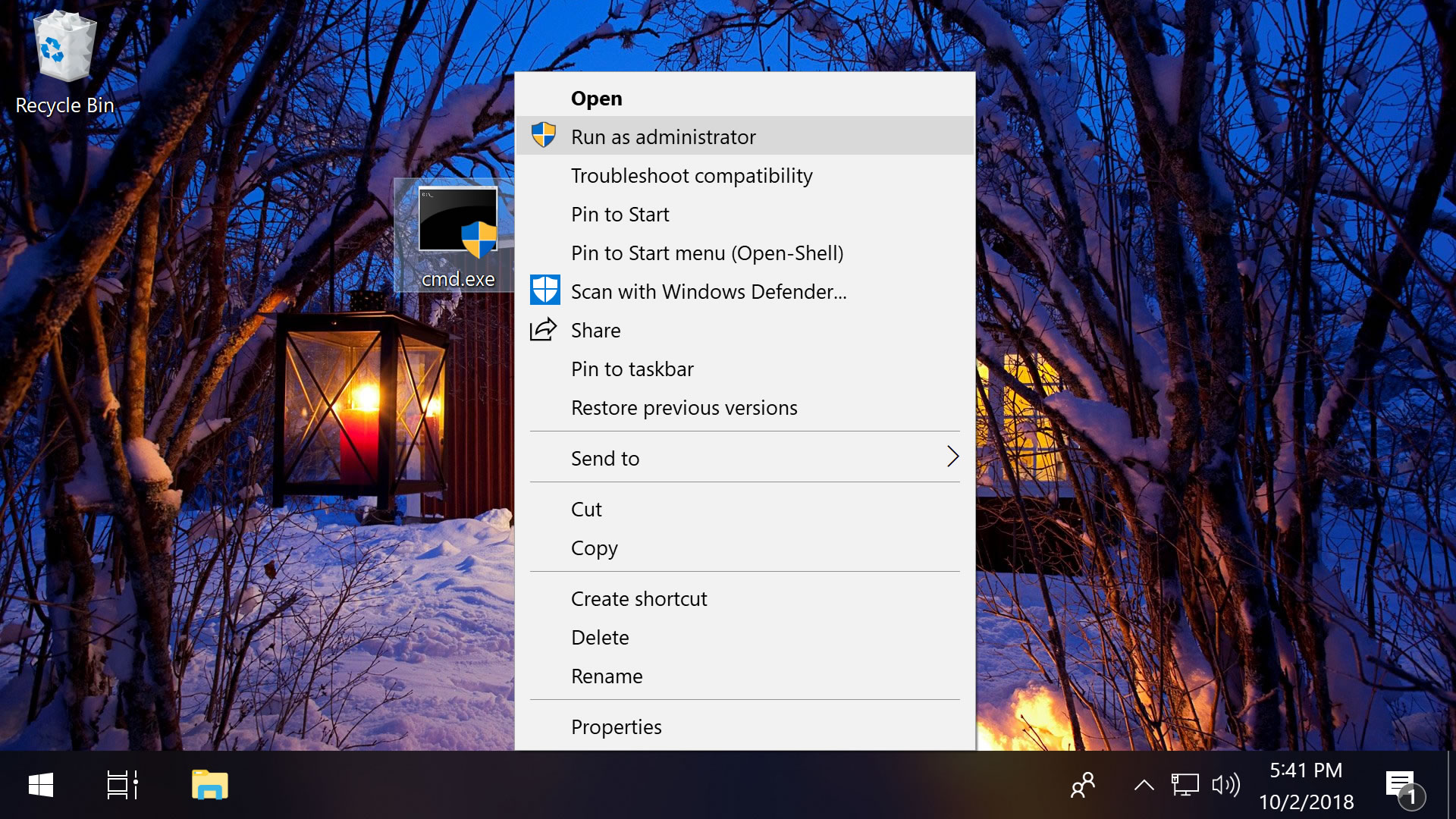
As a shortcut, holding Shift + Ctrl while double-clicking the file will also start the program as an admin.
Separately, holding only Shift while you right-click on the file will add "Run as a different user..." to the context menu, which opens a screen where you can enter another user's credentials, including the administrator account (the username is Administrator and may not have a password if you haven't applied one).
These locations also have shortcuts to admin access...
Start Menu: Right-click an executable like anywhere else for the option to launch a program as an administrator.
Taskbar: Click a program on your taskbar to open the jump list, then right-click the exe from that menu for the admin option.
File Explorer: Select the file in File Explorer > Click Manage in the Ribbon menu up top > Choose "Run as administrator."
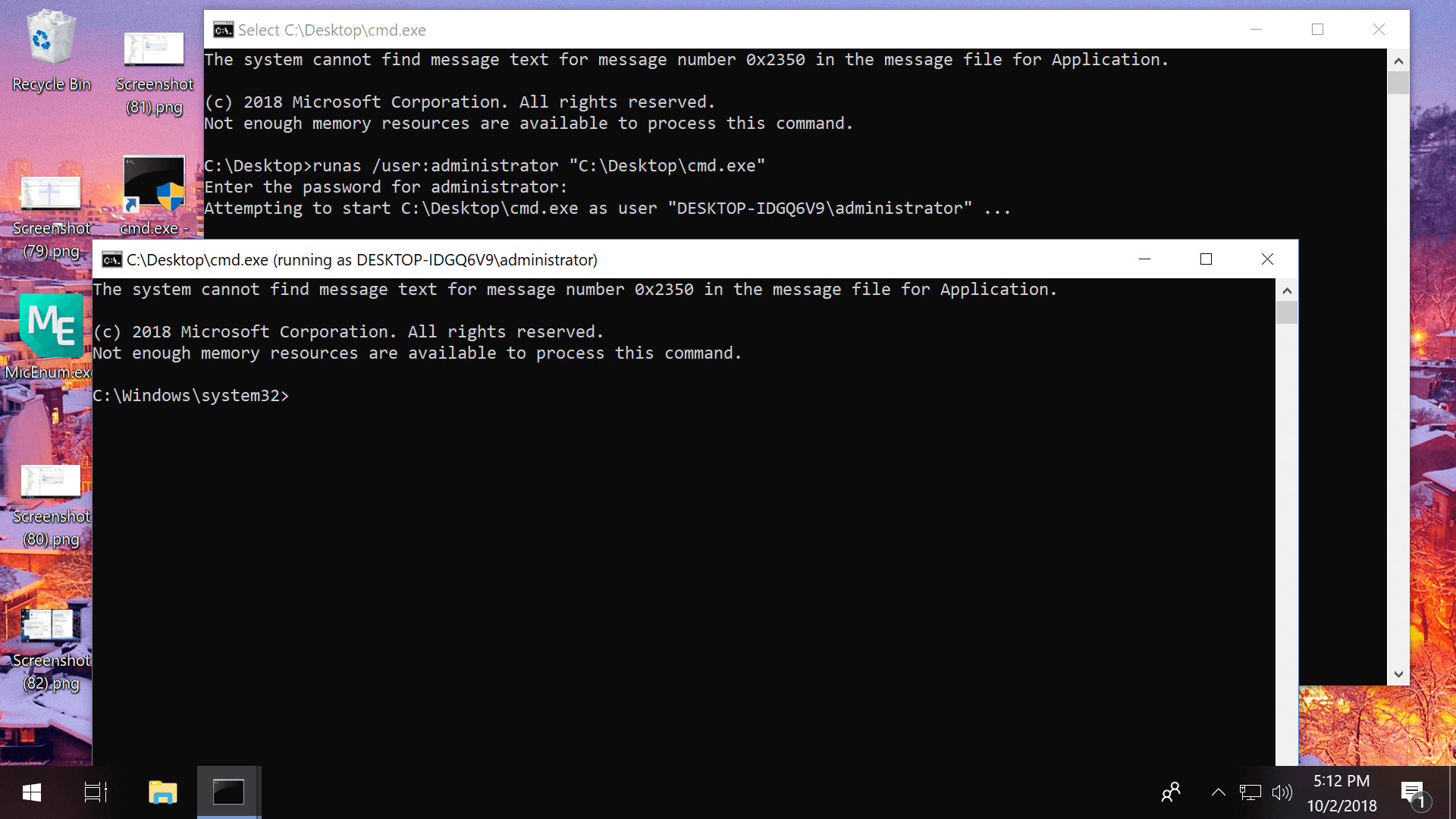
Run prompt: Enter this line into Run (Windows key + R): RunAs.exe /user:Administrator "cmd.exe"
Command Prompt: From the command line, enter this with your file location: runas /user:administrator "C:\Users\TechSpot\Desktop\file.exe"
Task Manager: Click File > Run new task > Check the box next to "Create this task with administrative privileges" > Enter the location of your file (example: C:\Users\TechSpot\Desktop\file.exe)
Task Scheduler: When creating a new task (Action > Create Task), enable these settings in the "General" tab: "Run whether user is logged on or not" and "Run with highest privileges"
Note that the Command Prompt method didn't work until we enabled the Administrator account and changed another setting that would allow the command to be entered without a password:
- Search Start or Run for compmgmt.msc > Go to Local Users and Groups > Users > double-click on Administrator and uncheck "Account is disabled"
- Search Start or Run for gpedit.msc > Go to Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Local Policies > Security Options > Double-click the option Accounts: Limit local account use of blank passwords to console logon online and choose Disable
Also, in the same section of the Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) that we just mentioned are a range of options to fine-tune Windows' User Account Control settings (scroll all the way down).
How to set programs so they always start as an admin
Given Microsoft's philosophy of providing programs with the least amount of access possible, configuring an application to always run as an administrator is generally not recommended but sometimes convenient when the software always requires elevation so you don't have to jump through those hoops every time. Here are a few ways to accomplish that:
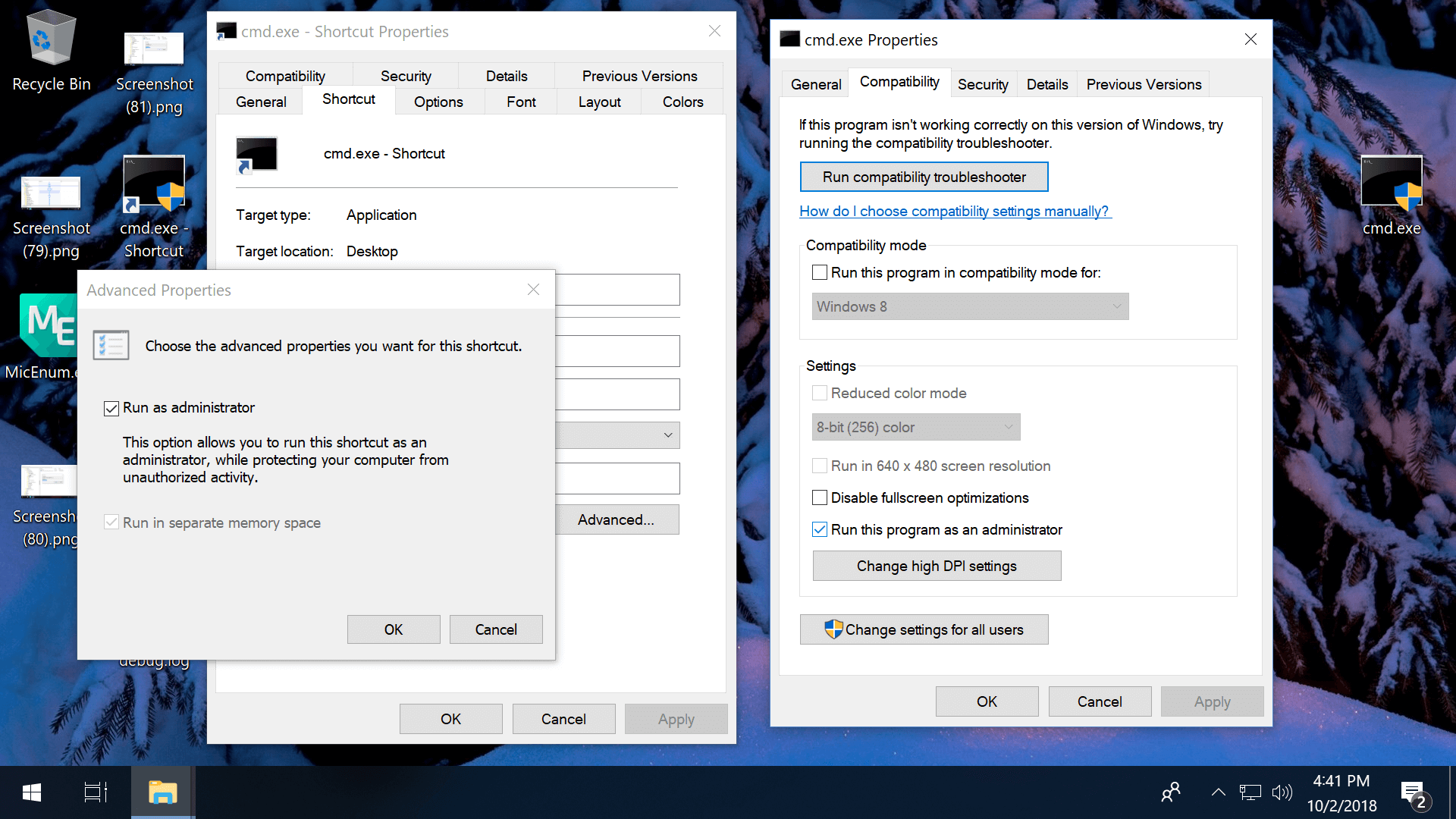
Always run as admin from a shortcut: Right-click on a shortcut file > Shortcut tab > Advanced > Check the box to "Run as administrator"
Note that you can create a shortcut file by right-clicking the main exe, and that if you copy the shortcut into C:\Users\TechSpot\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup the program will automatically start with Windows as you sign in.
Always run as admin via Compatibility Properties: Right-click on an exe > Properties > Compatibility tab > Check the box to "Run this program as an administrator."
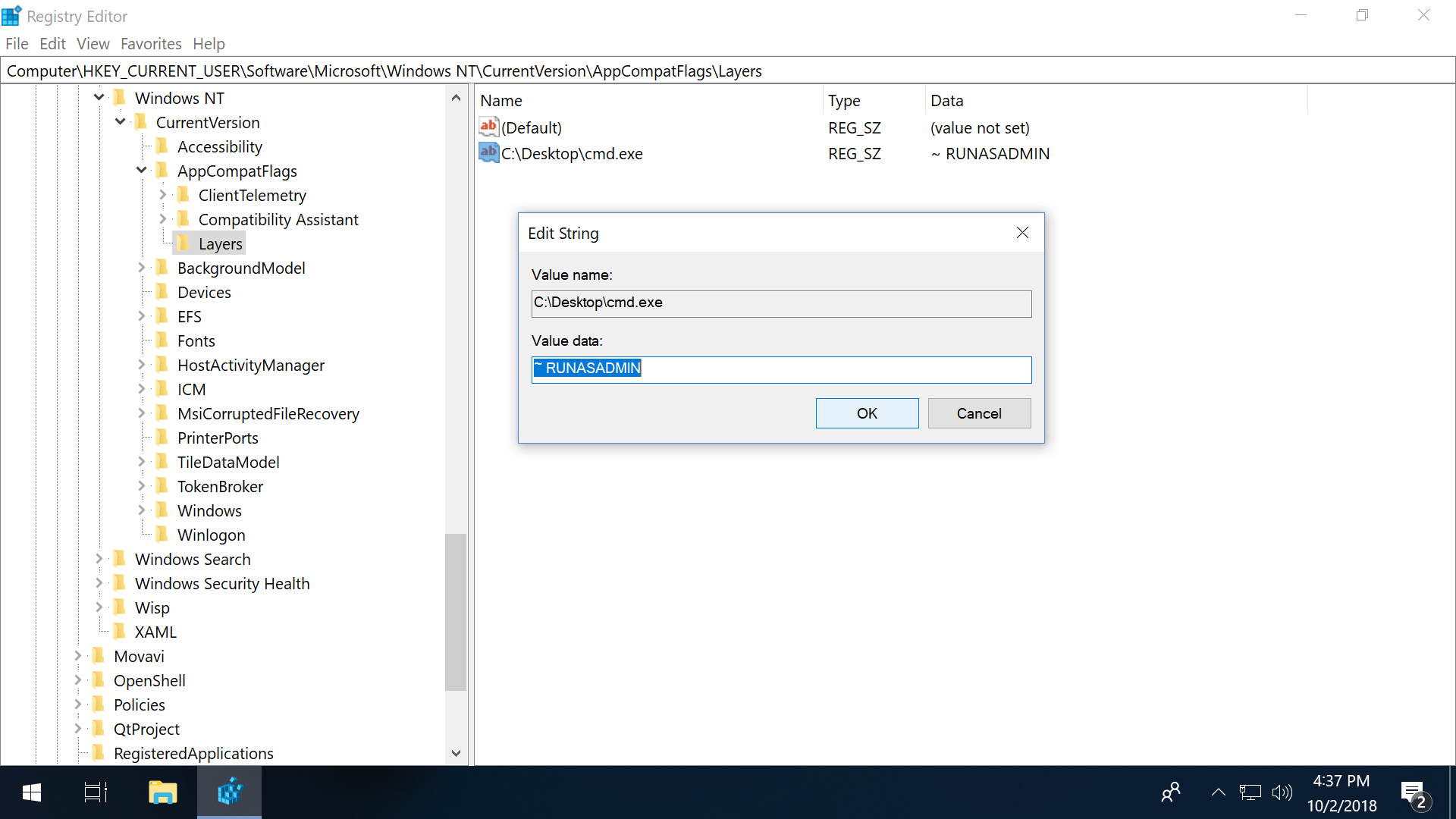
Always run as admin via the Registry Editor:
- Navigate to: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\AppCompatFlags\Layers
- If "Layers" is missing, right-click AppCompatFlags and add a new key named Layers
- Right-click Layers (either the folder or in the right pane) an create a new String Value
- Set the value name as the full path of the exe file
- Set value data as ~ RUNASADMIN
Bonus
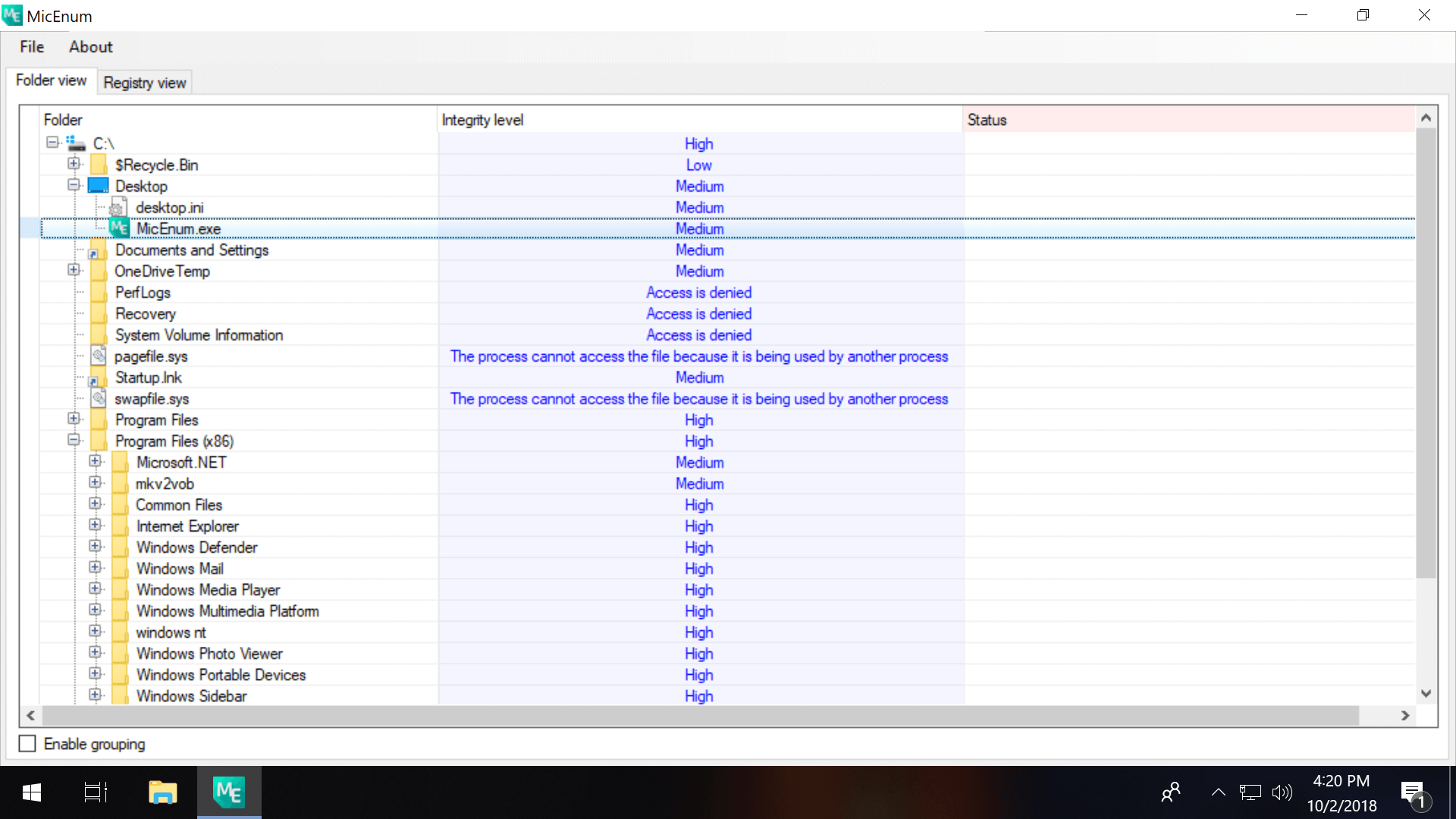
#1 Third-party software including MicEnum will generate a list of Windows files/folders and their integrity levels, including the ability to set a new integrity level as well as browse in both folder and registry views.
Process Explorer (pictured in the intro of this article) also has the ability to display integrity levels if you right click the horizontal bar with CPU, Private Bytes etc. and open the properties (check the box next to Integrity Levels).
#2 On a new Windows installation, the first user account created is a local administrator account while subsequent accounts are standard users. By default, the built-in administrator account is disabled. You can enable the account so it's available when you log in to Windows by entering this line into Command Prompt (use "no" to disable it again): net user administrator /active:yes
#3 Microsoft has different utilities such as Elevation PowerToys and PsExec which can also be used to gain administrator access but span beyond the scope of this guide.
"Run as Administrator": What Does It Mean?
Facebook Lite for Android 167.0.0.4
This official 'Lite' Facebook app is designed to be more efficient with data and work in all network conditions, especially slower mobile connections.
As featured in:
Keeping up with friends is faster and easier than ever with the Facebook Lite app! Use Facebook Lite as a friends app to connect and keep up with your social network. The Facebook Lite app is small, allowing you to save space on your phone and use Facebook in 2G conditions. Many of the classic features of Facebook are available on the app, such as sharing to a Timeline, liking photos, searching for people, and editing your profile and groups. Specific features include:
- Find friends and family
- Post status updates & use Facebook emoji to help relay what’s going on in your world
- Share photos and your favorite memes
- Get notified when friends like and comment on your posts
- Find local social events, RSVP, and make plans to meet up with friends
- Interact with your friends by adding your own comments or reactions to their Facebook posts
- Save photos by adding them to photo albums
- Follow people to get their latest news
- Look up local businesses to see reviews, operation hours, and pictures
The Facebook app does more than help you stay connected with your friends and interests. It's also your personal organizer for storing, saving and sharing photos. It's easy to share photos straight from your Android camera, and you have full control over your photos and privacy settings. You can choose when to keep individual photos private or even set up a secret photo album to control who sees it.
Facebook Lite also helps you keep up with the latest news and current events around the world. Subscribe to your favorite celebrities, brands, websites, artists, or sports teams to follow their News Feeds from the convenience of your Facebook Lite app!
Facebook Lite also helps you keep up with the latest news and current events around the world. Subscribe to your favorite celebrities, brands, websites, artists, or sports teams to follow their News Feeds from the convenience of your Facebook Lite app!
What's New:
- Improvements for reliability and speed.
For the full Facebook app, install Facebook for Android.
Facebook Lite for Android
Posted by : Admin
Now, Xiaomi is going to launch its new flagship device the Xiaomi Mi Edge Pro in 2020. This will be an upgraded version of Xiaomi Mi Edge. The main highlighted feature of this phone is its triple rare camera setup and Qualcomm Snapdragon 855+chipset. As far as design is concerned, it is made up of glass and it sports an on-screen selfie camera. The expected Xiaomi Mi Edge Pro price is Rs. 38,999 for the base variant, an amount that goes up to Rs. 42,999 for the variant which is having 10GB RAM and 512 GB internal storage. It will be dual SIM 5G LTE supportable smartphone which will run on Android 10 out of the box. Now let us talk about the main specifications and features of Mi Edge Pro.
Xiaomi Mi Edge Pro Full Specifications
The phone is expected to sport 6.5 inches super AMOLED touchscreen display with an aspect ratio of 19:9 having 1400 x 2960 pixels support. In terms of optics, the Edge Pro sports triple-camera setup, it features a 48.0 MP + 32.0 MP + 8.0MP sensors which will support autofocus and dual-LED flash, 4k HDR. Whereas on the front it sports on display selfie camera of 32.0 MP sensor. The total internal storage of this device is of 256/512 GB which can be further expanded up to 512GB. But it’s not having an extra slot for memory card, the card will be inserted inside Second SIM slot.
Xiaomi Mi Edge Pro Key Specs
| Display Size | 6.5 inches |
| Pixels | 1440 x 2960 |
| Processor | Octa-Core 2.8 GHz |
| Chipset | Qualcomm Snapdragon 855+ |
| Graphics | Mail G72 |
| RAM | 8/10 GB |
| Primary Camera | 48.0 MP + 32.0 MP + 8.0MP (Autofocus and Dual- LED flash, 4k HDR) |
| Secondary Camera | 32.0 MP |
| Memory | 256GB /512GB |
| Expandable Memory Upto | 512 GB |
| Sensors Used | Fingerprint, accelerometer, gyroscope, Compass/ Magnetometer, In-display |
| SIM 1 | 5G, 4G/ LTE, CDMA |
| SIM 2 | GSM, 4G/ LTE |
| Colours | Mirror Black, Midnight Blue, and Red |
| O.S | Android 10.0 |
| Battery | 6500 mAh |
The phone is powered up by 64-bit octa-core processor clocked at a frequency of 2.8 GHz on Qualcomm Snapdragon 855+ SOC and coupled with 8/10 GB of RAM. Sensors on the phones include an in-display fingerprint sensor, camera, Accelerometer, Gyroscope, proximity sensor, and an RGB light sensor. It’s backed by 6500 mAh non removable battery and which will support wireless fast charging.
Xiaomi Mi Edge Pro Price and Release Date
The 8GB of RAM and 256 GB memory variant is priced for Rs. 38,999 whereas the other one which will have 10GB RAM and 512 GB internal Storage is priced for Rs. 42,999 in India.
Xiaomi Mi Edge Pro Specifications, Price and Features
Best WordPress hosting services 2020 in the table below. Logo Plan Price/ month Features Support View Full Review Basic $2.95/mo. 1...